In today's competitive environment, the difference between thriving and merely surviving often lies in how effectively an organization runs. Operational excellence isn't just a corporate buzzword; it's a strategic imperative for any team aiming for sustainable growth and peak efficiency. Whether you're a nonprofit leader maximizing donor impact, an IT manager streamlining systems, or a small medical practice ensuring seamless patient care, the goal is the same: create a culture and implement systems that consistently deliver superior value. But where do you begin?
This guide cuts through the noise to provide a definitive, actionable roundup of the most impactful operational excellence best practices you can implement today. We move beyond abstract theory to provide a clear roadmap for tangible improvement. Each practice is broken down into specific implementation steps, common pitfalls to avoid, and real-world examples tailored to diverse sectors, including fundraising, healthcare administration, and technology operations.
Forget generic advice. You will learn precisely how to standardize workflows, leverage data for smarter decisions, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. We will explore everything from lean process optimization and integrated workflow automation to data centralization and strategic resource planning. This article is your blueprint to transform chaotic processes into a command center of efficiency, eliminate waste, and build a resilient, high-performing operation from the ground up. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of the essential frameworks needed to achieve and sustain operational excellence within your organization.
1. Lean Process Optimization
Lean process optimization is a foundational operational excellence best practice dedicated to maximizing value by systematically eliminating waste. Originating from Toyota's production system, this methodology scrutinizes every step of a workflow to identify and remove activities that consume resources without adding value for the end customer or beneficiary. For service-oriented organizations like nonprofits and medical practices, this means cutting redundant administrative tasks, reducing operational costs, and accelerating service delivery without compromising quality.
The core principle involves identifying the "eight wastes" of Lean: defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra-processing. By addressing these, organizations can streamline operations and focus on what truly matters.
Why It's a Top Practice
Lean is highly effective because it provides a structured, repeatable framework for improvement that empowers employees at all levels. It shifts the organizational mindset from "this is how we've always done it" to "how can we do this better?" This focus on continuous improvement (Kaizen) builds a resilient and adaptive culture.
A medical practice, for example, can use Lean to streamline its patient intake process, significantly reducing wait times and improving patient satisfaction. Similarly, a nonprofit can apply Lean principles to its grant administration workflow, cutting overhead by 25% and redirecting those savings toward its core mission.
How to Implement Lean Process Optimization
- Identify a Target Process: Don't try to overhaul everything at once. Select a single, high-impact process, such as patient scheduling, grant reporting, or donor acknowledgments.
- Map the Current State: Visually map every step of the chosen process. Involve the frontline staff who execute these tasks daily, as they have the clearest view of existing inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Identify and Categorize Waste: Analyze the process map to pinpoint non-value-adding activities. Is there unnecessary paperwork? Are staff members waiting for information? Are multiple systems being used for one task?
- Design the Future State: Redesign the process to eliminate the identified waste. This could involve simplifying steps, automating tasks, or reorganizing responsibilities.
- Implement and Measure: Roll out the new process and track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure its impact. Use metrics established before the change to demonstrate a clear return on investment.
Key Insight: The most successful Lean initiatives are driven from the ground up. Empowering frontline teams to identify and solve problems builds momentum and ensures that improvements are practical and sustainable.
2. Integrated Workflow Automation
Integrated workflow automation is an essential operational excellence best practice focused on connecting disparate business systems and processes into a single, cohesive workflow. This practice eliminates manual handoffs, data entry errors, and information silos by creating automated sequences that trigger actions across multiple applications. For organizations like nonprofits and medical practices that rely on various tools, including Google Workspace, automation frees skilled staff from repetitive, low-value tasks to concentrate on strategic, mission-critical work.
The core objective is to ensure that when a task is completed in one system, the next step is automatically initiated in another, creating a seamless operational flow. This drastically accelerates processes, improves data accuracy, and enhances overall efficiency.
Why It's a Top Practice
Automation delivers a direct and measurable return on investment by boosting productivity and reducing operational friction. It empowers small teams to manage complex, high-volume processes that would otherwise require significant manual effort. This scalability is crucial for growing organizations aiming to do more with limited resources.
For instance, a nonprofit can use OpsHub to automate its entire grant application process, from initial form submission to final tracking and reporting. A medical practice can automate patient appointment reminders, intake form collection, and even billing reconciliation, leading to fewer no-shows and a more streamlined patient experience.
How to Implement Integrated Workflow Automation
- Map Current Workflows: Before automating, thoroughly document a target process, like donor acknowledgments or patient onboarding. Identify every manual step, handoff, and potential bottleneck.
- Prioritize High-Impact Tasks: Start with high-volume, rule-based, and repetitive tasks. Automating these provides quick wins and builds momentum for more complex projects.
- Select the Right Tools: Choose an automation platform that integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, such as your CRM, accounting software, and Google Workspace.
- Design and Document the Automation: Clearly define the triggers, actions, and logic for the automated workflow. Document these rules so the team can understand, manage, and troubleshoot the automation.
- Monitor and Refine: Track performance metrics to confirm the automation is working as intended. Be prepared to adjust the rules based on real-world outcomes and evolving business needs.
Key Insight: The goal of automation is not to replace people but to augment their capabilities. The most effective automation strategies focus on handling tedious tasks, freeing up human talent for complex problem-solving and high-value interactions.
3. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics-Driven Management
Metrics-driven management is an operational excellence best practice centered on the principle that "what gets measured gets managed." It involves establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to translate strategic objectives into measurable, trackable outcomes. This approach shifts decision-making from intuition to data, creating a culture of accountability and continuous, targeted improvement. For organizations like nonprofits and medical practices, KPIs provide clear visibility into operational health and mission impact.
This practice empowers teams to monitor progress in real-time, identify performance gaps, and allocate resources more effectively. By defining what success looks like in quantifiable terms, organizations can align every action and team toward common goals, ensuring that daily efforts directly contribute to the larger strategic vision.
Why It's a Top Practice
A metrics-driven approach provides an objective, shared language for performance. It removes ambiguity and ensures everyone understands the priorities and how their work contributes. This clarity is essential for aligning teams, justifying investments, and demonstrating value to stakeholders, whether they are donors, patients, or board members.
For instance, a medical practice can track KPIs like patient satisfaction scores and appointment no-show rates to identify service delivery issues and improve patient retention. A nonprofit fundraising team can monitor donor retention rates and cost-per-dollar-raised to optimize campaign strategies and maximize their financial efficiency.
How to Implement KPIs and Metrics-Driven Management
- Define Strategic Objectives: Start with your high-level goals. What are the most critical outcomes for your organization over the next year? Examples include improving patient outcomes, increasing donor engagement, or securing more grant funding.
- Select a Few Core KPIs: Identify 5-7 key metrics that directly reflect progress toward these objectives. Avoid "vanity metrics" and focus on numbers that drive action. Ensure each KPI is SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Establish Baselines and Targets: Measure your current performance to create a baseline for each KPI. Then, set realistic but ambitious targets for improvement.
- Create Visual Dashboards: Use tools to build simple, visual dashboards that make KPI performance instantly understandable to everyone. This transparency keeps the team informed and engaged with the metrics.
- Implement a Review Cadence: Schedule regular meetings to review the KPIs. Discuss progress, analyze trends, and decide on corrective actions. A typical rhythm is a monthly leadership review and a quarterly all-hands update.
Key Insight: The power of KPIs lies not in the data itself, but in the conversations and actions it inspires. Use your metrics as a starting point for strategic discussions about what is working, what isn't, and where to focus next.
4. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and Documentation
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and documentation are the backbone of operational excellence, providing a clear, consistent, and repeatable framework for every critical task. This practice involves creating comprehensive, accessible guides that detail the exact steps for completing specific processes. For organizations like medical practices and nonprofits, where consistency and compliance are paramount, well-documented procedures reduce errors, ensure quality, and simplify training.
The core principle is to capture institutional knowledge, turning implicit expertise into explicit, shareable resources. This is essential for organizations managing volunteer turnover, training new medical staff, or scaling operations without sacrificing quality. SOPs transform ambiguity into a reliable roadmap that anyone can follow.
Why It's a Top Practice
Effective documentation is a powerful operational excellence best practice because it builds a foundation of stability and predictability. It eliminates guesswork and empowers team members to perform their roles confidently and correctly, even when faced with unfamiliar tasks. This consistency is crucial for maintaining high standards of service and meeting regulatory requirements.
For instance, a medical practice can use an SOP for its patient intake workflow to ensure every patient receives the same high level of care and that all necessary compliance steps are met. A nonprofit can document its grant application process, enabling volunteers to complete complex submissions accurately and increasing the chances of securing funding.
How to Implement SOPs and Documentation
- Prioritize Critical Processes: Identify the tasks that have the highest impact on quality, compliance, or efficiency. Focus on areas like patient billing, volunteer onboarding, or donor data management first.
- Involve the Experts: Engage the frontline staff who perform these tasks daily. Their direct input is invaluable for creating SOPs that are practical, accurate, and easy to understand.
- Standardize the Format: Use a consistent template for all SOPs, including sections for purpose, scope, responsibilities, step-by-step instructions, and review dates. Use simple language and visual aids where possible.
- Make SOPs Accessible: Store all documentation in a centralized, searchable location like a shared drive, internal wiki, or a platform like OpsHub. Ensure everyone knows where to find the most current versions.
- Establish a Review Cadence: Assign an owner to each SOP and schedule regular reviews (e.g., quarterly or annually) to ensure the documentation remains up-to-date with any process changes.
Key Insight: The best SOPs explain not just the 'how' but also the 'why.' When team members understand the purpose behind a procedure, they are more likely to follow it correctly and suggest meaningful improvements.
5. Cross-Functional Collaboration and Communication
Cross-functional collaboration is an operational excellence best practice focused on breaking down departmental silos to foster innovation, agility, and a unified organizational purpose. Instead of operating as independent units, teams from different functional areas (like clinical, administrative, and billing) work together toward shared objectives. This approach ensures that diverse perspectives inform decision-making, leading to more robust solutions and streamlined workflows.
For nonprofits and medical practices, where outcomes depend on coordinated effort, this practice is critical. It moves organizations away from fragmented communication and toward a cohesive system where knowledge is shared freely, conflicts are resolved quickly, and everyone is aligned on the mission. This integration ensures that every part of the organization works in concert, enhancing overall effectiveness and service delivery.
Why It's a Top Practice
Effective collaboration directly combats one of the biggest drains on efficiency: the friction caused by departmental silos. When teams are aligned, processes flow smoothly, reducing delays and redundant work. This practice builds a culture of shared ownership and accountability, where the organization's success is seen as a collective responsibility rather than a series of individual tasks.
For example, a nonprofit can align its program and development teams to create powerful donor impact reports that directly link fundraising efforts to tangible outcomes. A medical practice can bring clinical, administrative, and billing staff together to redesign the patient journey, ensuring a seamless experience from appointment scheduling to final payment.
How to Implement Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Define Shared Goals: Start by identifying a key organizational objective that requires input from multiple departments, such as improving patient satisfaction scores or increasing donor retention rates.
- Form Cross-Functional Teams: Assemble a dedicated team with representatives from each relevant department. Grant this team the authority to make decisions and implement changes related to the shared goal.
- Establish a Communication Cadence: Implement structured communication channels. This could include daily stand-ups for urgent projects, weekly team syncs for progress updates, and monthly reviews to assess strategic alignment.
- Utilize Shared Technology: Adopt collaborative platforms to create a single source of truth for project information. Tools that centralize documents, tasks, and communication prevent misinterpretations and keep everyone on the same page.
- Measure and Reinforce: Track the success of collaborative initiatives through project outcomes and employee feedback. Celebrate cross-functional wins to reinforce the value of this approach and encourage broader adoption.
Key Insight: True collaboration is more than just holding meetings. It requires creating a psychological safety net where team members feel empowered to share ideas, challenge assumptions, and contribute their unique expertise without fear of judgment.
6. Data Centralization and Analytics
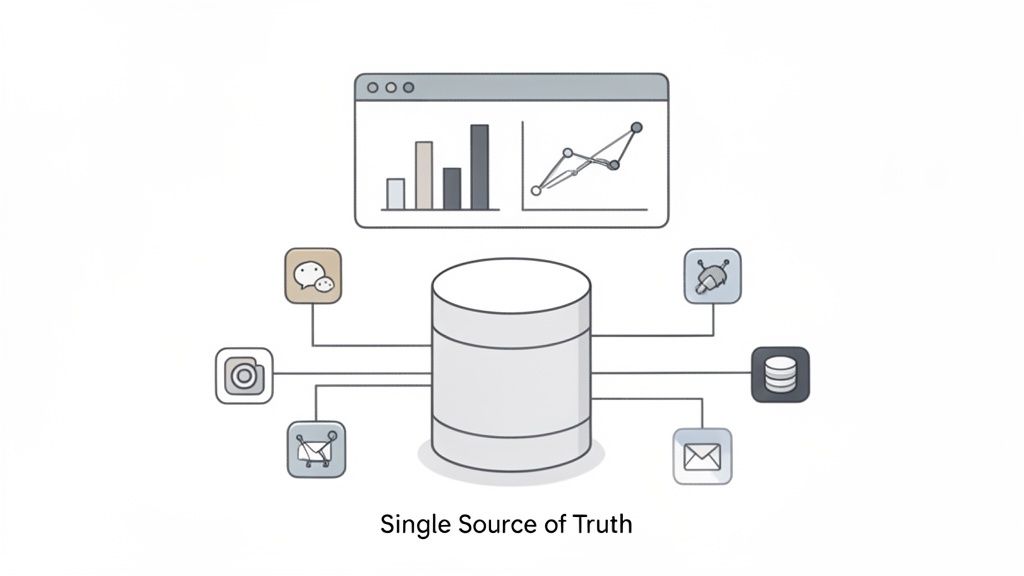
Data centralization and analytics is an operational excellence best practice focused on consolidating disparate data into a single, unified system. This creates a "single source of truth," eliminating the inefficiencies and errors caused by scattered spreadsheets, siloed software, and disconnected information. By centralizing data, organizations can uncover actionable insights, track performance accurately, and make informed strategic decisions.
This approach transforms raw data from a liability into a strategic asset. It empowers leaders to see clear patterns, predict future trends, and optimize resource allocation with confidence, moving beyond guesswork and intuition.
Why It's a Top Practice
Data centralization is critical because it provides the comprehensive visibility needed for true operational control. Without it, teams operate with incomplete pictures, leading to duplicated efforts, missed opportunities, and flawed strategies. A single source of truth ensures everyone is working from the same information, fostering alignment and accountability.
For example, a nonprofit can centralize donor and program data to precisely demonstrate impact to funders, securing larger grants. A medical practice with integrated patient records can reduce redundant testing and improve care coordination, directly enhancing patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
How to Implement Data Centralization and Analytics
- Map Data Sources: Begin by identifying and mapping all existing data sources across the organization. This includes everything from CRM software and financial systems to simple spreadsheets.
- Establish Data Governance: Create clear policies defining who owns the data, who can access it, and how data quality will be maintained. This foundational step prevents future chaos.
- Prioritize and Consolidate: Choose a high-value area to start, like unifying donor information or patient intake forms. Invest in cleaning and standardizing the data before moving it to a central repository.
- Implement a Central Hub: Select a platform or system, like a data warehouse or an integrated operations hub, to serve as your central repository. Use automated pipelines to feed data into the system, eliminating manual updates.
- Build Role-Based Dashboards: Create customized dashboards that provide relevant insights for different roles. Executives need high-level overviews of financial health, while program managers require detailed operational metrics.
Key Insight: The goal is not just to collect data but to make it accessible and actionable. A successful data centralization strategy empowers your team to ask better questions and get clear, reliable answers quickly.
7. Continuous Improvement Culture and Change Management
Embedding a culture of continuous improvement is a powerful operational excellence best practice that transforms how an organization evolves. This approach, often called Kaizen, makes incremental improvement a daily habit rather than a one-time project. It systematically identifies opportunities, tests solutions, learns from failures, and scales successes. For nonprofits maximizing limited resources or medical practices adapting to changing regulations, continuous improvement ensures long-term relevance, efficiency, and resilience.
The core principle is that small, ongoing positive changes can reap major benefits over time. It relies on the idea that employees closest to a process are best equipped to improve it, fostering a sense of ownership and engagement across the entire organization.
Why It's a Top Practice
A continuous improvement culture creates a proactive, problem-solving workforce that is resilient to change. Instead of reacting to crises, the organization constantly seeks better ways to operate, leading to sustained performance gains. This practice moves beyond isolated projects to build a self-perpetuating cycle of excellence.
For instance, a medical clinic can use rapid-cycle improvement projects (like the Plan-Do-Check-Act model) to systematically test changes to its scheduling process, steadily reducing patient wait times. A nonprofit can establish formal volunteer feedback loops, using suggestions to drive program enhancements that better serve its community.
How to Implement a Continuous Improvement Culture
- Secure Leadership Buy-In: Leadership must champion the culture by providing resources, celebrating wins, and framing failures as learning opportunities. Their commitment sets the tone for the entire organization.
- Provide Structured Frameworks: Equip teams with simple, proven methodologies like PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act). This provides a common language and a clear process for identifying, testing, and implementing improvements.
- Empower Frontline Staff: Train employees in basic problem-solving and process improvement techniques. Allocate dedicated time for improvement work so it becomes part of their role, not an extra burden.
- Promote Psychological Safety: Create an environment where it is safe to experiment and fail. Punishing mistakes will stifle innovation and discourage participation. Instead, analyze what went wrong and apply the lessons learned.
- Visualize and Celebrate Progress: Make improvement efforts visible through team huddle boards or digital dashboards. Publicly celebrate both small and large wins to build momentum and reinforce desired behaviors.
Key Insight: True continuous improvement is a cultural shift, not a management initiative. It thrives when every team member feels empowered and responsible for making their corner of the organization better every day.
8. Resource Optimization and Capacity Planning
Resource optimization is a critical operational excellence best practice focused on the strategic allocation of limited resources-people, budget, technology, and time-to achieve maximum impact. It is paired with capacity planning, which involves aligning an organization's workload with its available resources to prevent bottlenecks, reduce employee burnout, and ensure sustainable performance. For organizations operating with tight constraints, like nonprofits or medical practices, this means making every dollar, hour, and team member count.
This practice moves beyond simple scheduling; it's a forward-looking strategy for understanding what your team can realistically accomplish. It helps prevent overcommitment and ensures that resources are directed toward the activities that deliver the most value to your mission or patients.
Why It's a Top Practice
Effective resource optimization and capacity planning transform reactive, fire-fighting cultures into proactive, strategic ones. It provides leaders with the visibility needed to make informed decisions about taking on new projects, pursuing grants, or expanding services. This clarity is essential for sustainable growth and preventing the high costs associated with employee turnover and inefficient resource use.
For instance, a medical practice can use capacity planning to optimize provider schedules, minimizing patient wait times and costly staff overtime. A nonprofit can allocate its limited fundraising staff to the highest-potential campaigns, significantly boosting its return on investment and programmatic funding.
How to Implement Resource Optimization and Capacity Planning
- Create Resource Visibility: Start by gaining a clear, centralized view of what everyone is working on. Use project management tools or time-tracking software to understand current workloads and commitments across the organization.
- Establish Capacity Benchmarks: Determine how much productive work can realistically be completed. Analyze historical data to understand the time required for key tasks and build benchmarks for individuals and teams, accounting for administrative overhead and non-project work.
- Conduct Regular Capacity Reviews: Don't treat planning as a one-time event. Hold quarterly reviews to match projected workloads with available resources, identify potential gaps, and adjust priorities before they become crises.
- Develop a Prioritization Framework: Create a simple, clear system for ranking tasks and projects based on strategic importance and impact. This ensures that when resources are limited, teams are always focused on the most critical work.
- Plan for Fluctuations: Proactively account for variables like staff turnover, seasonal demand spikes, or vacation time. Build contingency plans to maintain operational stability during these predictable shifts in capacity.
Key Insight: True capacity planning isn't just about avoiding over-allocation. It's about creating a culture where it is safe to say 'no' to low-impact work, empowering teams to protect their focus and energy for what matters most.
9. Quality Assurance and Risk Management
Quality assurance and risk management are intertwined operational excellence best practices focused on proactively preventing problems and preparing for potential disruptions. Quality assurance establishes systematic checks to ensure services and deliverables consistently meet predefined standards. Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to the organization's operations, finances, and reputation. For organizations handling sensitive information or providing critical services, this dual approach is non-negotiable.
This practice moves organizations from a reactive, crisis-driven mode to a proactive, prepared state. It’s about building resilience and dependability into the very fabric of your operations, ensuring stability even when faced with uncertainty.
Why It's a Top Practice
This integrated approach is critical because it directly protects an organization’s most valuable assets: its reputation, stakeholder trust, and ability to deliver on its mission. It prevents costly errors, safeguards sensitive data, and ensures service continuity. A failure in either area can lead to compliance violations, financial loss, or irreparable damage to constituent relationships.
For example, a medical practice that implements robust quality assurance, like credential verification and infection control protocols, directly protects patient safety. A nonprofit that uses risk management to create strong financial controls and donor privacy policies safeguards its funding and community trust, ensuring long-term viability.
How to Implement Quality Assurance and Risk Management
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Systematically identify potential threats to your organization. Categorize them by likelihood and potential impact to prioritize which risks to address first, such as data breaches, funding shortfalls, or compliance failures.
- Integrate Quality Checks: Build quality control steps directly into your key processes. Instead of relying solely on final inspections, implement checks at critical stages, like verifying data entry accuracy or confirming donor information before sending communications.
- Develop Clear Incident Protocols: Create and communicate simple procedures for reporting issues or potential risks. Staff should feel empowered to flag problems early without fear of blame. The goal is rapid identification and resolution.
- Perform Root Cause Analysis: When a failure or quality issue occurs, investigate its fundamental cause. This shifts the focus from blaming individuals to fixing the underlying systemic weakness, preventing the problem from recurring.
- Create and Test a Continuity Plan: Develop a formal business continuity plan that outlines how your organization will operate during a significant disruption. Test this plan at least annually to ensure it is effective and that your team knows how to execute it.
Key Insight: Quality and risk management are not one-time projects; they are ongoing disciplines. True operational excellence is achieved when a culture of proactive risk awareness and commitment to quality is embedded at every level of the organization.
10. Technology Enablement and System Integration
Technology enablement is a strategic operational excellence best practice focused on using integrated systems to amplify efficiency and support growth. Instead of adopting tools in isolated silos, this approach connects mission-critical software to create a unified ecosystem. For organizations relying on Google Workspace, electronic health records (EHRs), or donor CRMs, this integration is key to reducing manual data entry, improving information flow, and gaining a comprehensive view of operations.
This practice moves beyond simply having technology; it's about making technology work together seamlessly. When systems are integrated, data entered in one platform automatically updates others, creating a single source of truth and eliminating the errors and delays associated with fragmented information.
Why It's a Top Practice
Integrated technology is a force multiplier for every other operational excellence initiative. It provides the digital backbone that makes process optimization, data-driven decisions, and automation possible. It prevents technology from becoming a bottleneck and instead turns it into an asset that enhances productivity and provides clear operational visibility.
For example, a medical practice that integrates its EHR system with billing and patient communication platforms can automate appointment reminders and streamline insurance claims, freeing up staff for patient care. Likewise, a nonprofit connecting its grant management tool with its CRM and financial software gains a real-time, 360-degree view of funding, program impact, and donor engagement.
How to Implement Technology Enablement and System Integration
- Map Your Core Workflows: Before choosing any tool, map out your essential processes. Identify where data is created, how it moves between teams, and where manual handoffs create friction.
- Audit Your Existing Tech Stack: Evaluate your current tools. What is working well? Where are the data silos? Identify the most critical systems that must be integrated, such as your CRM, financial software, or project management platform.
- Prioritize Integration Capabilities: When selecting new software, make integration a primary decision factor. Look for tools with robust APIs, pre-built connectors (like those offered by Zapier or Make), or platforms like OpsHub that are designed as a unified system from the start.
- Implement in Phases: Don't try to connect everything at once. Start with a high-impact integration, such as connecting your donor database to your email marketing tool, and build from there.
- Plan for Change Management: New technology requires training and support. Communicate the benefits of the integrated system and provide resources to help your team adapt to the new, more efficient workflows.
Key Insight: Don't let your technology dictate your processes. A successful integration strategy starts with understanding your operational needs and then selecting tools that fit into and enhance your ideal workflow, not the other way around.
Operational Excellence: 10-Practice Comparison
| Item | Implementation complexity 🔄 | Resource requirements ⚡ | Expected outcomes 📊 | Ideal use cases 💡 | Key advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lean Process Optimization | Medium–High 🔄🔄🔄 — cultural change & training | Moderate ⚡⚡ — time & facilitator resources | Lower costs, faster processes, higher satisfaction 📊 | Process-heavy orgs (clinics, nonprofits) 💡 | Eliminates waste; boosts speed & engagement ⭐ |
| Integrated Workflow Automation | High 🔄🔄🔄 — integrations & configuration | Moderate–High ⚡⚡⚡ — tools & technical setup | Vastly reduced manual work; faster cycle times 📊 | Multi-system workflows, Google Workspace users 💡 | Reduces errors; frees staff; highly scalable ⭐ |
| KPIs & Metrics-Driven Management | Medium 🔄🔄 — metric selection & setup | Low–Moderate ⚡⚡ — dashboards & data collection | Clear visibility; data-driven decisions & accountability 📊 | Impact measurement, grant reporting, performance tracking 💡 | Aligns teams; detects issues early ⭐ |
| SOPs & Documentation | Medium 🔄🔄 — creation & governance | Low–Moderate ⚡⚡ — staff time to author & maintain | Consistent quality; faster onboarding; fewer errors 📊 | High-turnover teams, compliance-heavy practices 💡 | Standardizes work; preserves knowledge ⭐ |
| Cross-Functional Collaboration & Communication | Medium 🔄🔄 — coordination & facilitation | Low–Moderate ⚡⚡ — meeting time & shared tools | Better decisions; less rework; improved innovation 📊 | Cross-department initiatives; program + fundraising alignment 💡 | Diverse perspectives; faster problem resolution ⭐ |
| Data Centralization & Analytics | High 🔄🔄🔄 — ETL, modeling, governance | High ⚡⚡⚡ — infrastructure & analytics expertise | Single source of truth; predictive insights; faster reporting 📊 | Organizations with scattered data needing unified insights 💡 | Eliminates silos; enables forecasting & accuracy ⭐ |
| Continuous Improvement Culture & Change Management | High 🔄🔄🔄 — sustained cultural effort | Moderate–High ⚡⚡⚡ — training, leadership time | Incremental compounding gains; higher engagement over time 📊 | Orgs pursuing long-term adaptability & resilience 💡 | Builds ownership; continuous performance gains ⭐ |
| Resource Optimization & Capacity Planning | Medium 🔄🔄 — analysis & tooling | Moderate ⚡⚡ — planning tools & honest data | Balanced workload; reduced burnout; better delivery 📊 | Small teams, seasonal workloads, scheduling-intensive orgs 💡 | Maximizes ROI on people & tools; prevents overload ⭐ |
| Quality Assurance & Risk Management | Medium–High 🔄🔄🔄 — controls & audits | Moderate–High ⚡⚡⚡ — compliance expertise & monitoring | Fewer incidents; regulatory compliance; faster recovery 📊 | Healthcare, data-sensitive, and highly regulated environments 💡 | Protects reputation, assets, and ensures compliance ⭐ |
| Technology Enablement & System Integration | High 🔄🔄🔄 — architecture & interoperability | High ⚡⚡⚡ — platforms, integration, maintenance | Streamlined workflows; consistent data; improved productivity 📊 | Orgs needing integrated SaaS stacks (EHRs, CRM, Workspace) 💡 | Enables automation, reduces switching, scales operations ⭐ |
Your Unified Command Center for Operational Excellence
Navigating the landscape of operational excellence can feel like assembling a complex machine with many moving parts. From Lean Process Optimization and Integrated Workflow Automation to Data Centralization and fostering a Continuous Improvement Culture, each of the ten best practices we have explored serves as a critical component. Implementing them in isolation yields incremental gains, but their true, transformative power is unlocked only when they are integrated into a cohesive, interconnected system.
The journey toward operational excellence is not a finite project with a clear endpoint; it is a fundamental shift in organizational culture and daily habits. It’s about building a resilient, adaptable framework that empowers your team to deliver consistent value, whether you are a non-profit leader managing grants, a COO optimizing workflows in a small medical practice, or a fundraiser striving for greater donor impact. The core challenge lies in orchestrating these distinct practices so they function as a single, harmonious engine driving your mission forward.
From Disparate Practices to an Integrated System
The ultimate goal is to move beyond a checklist of operational excellence best practices and create a living, breathing ecosystem where efficiency, clarity, and collaboration are the default. This is where many organizations falter, struggling to connect the dots between their documented SOPs, their real-time performance metrics, and the cross-functional teams executing the work. Without a central nervous system, even the best-laid plans can devolve into siloed efforts and fragmented data.
Consider the interplay between the principles discussed:
- Process Mapping and SOPs are static documents until they are embedded into Automated Workflows.
- Metrics-Driven Management is impossible without clean, centralized Data and Analytics.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration thrives when everyone has access to the same information and a clear view of shared objectives, which is enabled by Technology Integration.
This interconnectedness is the key. You need a platform that doesn’t just support one of these pillars but unites all of them, providing a single source of truth and a command center for your entire operation.
Activating Excellence with a Unified Hub
The transition from theory to practice requires a tool built on the very principles of operational excellence. Your team needs an intuitive environment where standardized processes are easy to follow, performance is transparent, and collaboration is seamless. This unified hub becomes the tangible manifestation of your commitment to continuous improvement, turning aspirational goals into measurable, daily actions.
By centralizing communication, tasks, data, and documentation, you eliminate the friction that stifles productivity. Non-profit leaders can track grant lifecycles from application to reporting in one place. Med spa managers can ensure consistent client experiences by standardizing treatment protocols and follow-ups. IT leaders can orchestrate complex projects with full visibility, ensuring resources are allocated effectively. This is where operational strategy meets execution.
Key Takeaway: The pinnacle of operational excellence is not just doing individual things right, but creating a system where all the right things happen together, consistently and effortlessly.
Mastering these concepts is no longer a competitive advantage; it is a requirement for sustainable growth and impact in any field. By weaving these operational excellence best practices into the fabric of your organization, you build a foundation that is not only efficient but also remarkably resilient, capable of adapting to new challenges and seizing future opportunities with confidence and clarity. The result is an organization that works smarter, not harder, empowering every team member to contribute their best work toward a shared vision.
Ready to transform these principles into your daily reality? OpsHub is the all-in-one platform designed to be your operational command center, integrating your people, processes, and data seamlessly. Discover how you can implement these operational excellence best practices with a unified system by exploring OpsHub today.